自Batch Norm出现之后,Layer Norm和Weight Norm作为Batch Norm的变体相继出现。最近又出来一个很”简单”的激活函数Selu,能够实现automatic rescale and shift。这些结构都是为了保证网络能够堆叠的更深的基本条件之一。除了这四种,还有highway network与resnet。
Batch Norm
BN对某一层激活值做batch维度的归一化,也就是对于每个batch,该层相应的output位置归一化所使用的mean和variance都是一样的。
- BN的学习参数包含rescale和shift两个参数;训练的时候不断更新这两个参数和moving average mean and variance
- BN在单独的层级之间使用比较方便,比如CNN
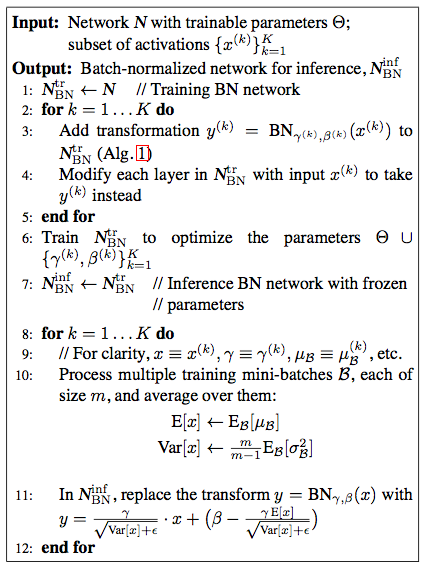
- 像RNN这样unroll之后层数不定,直接用BN不太方便,需要对每一层(每个time step)做BN,并保留每一层的mean和variance。不过由于RNN输入不定长(time step长度不定),可能会有validation或test的time step比train set里面的任何数据都长,因此会造成mean和variance不存在的情况。针对这个情况,需要对每个time step独立做统计。在BN-LSTM中是这么做的:Generalizing the model to sequences longer than those seen during training is straightforward thanks to the rapid convergence of the activations to their steady-state distributions (cf. Figure 5). For our experiments we estimate the population statistics separately for each timestep 1, . . . , Tmax where Tmax is the length of the longest training sequence. When at test time we need to generalize beyond Tmax, we use the population statistic of time Tmax for all time steps beyond it. During training we estimate the statistics across the minibatch, independently for each timestep. At test time we use estimates obtained by averaging the minibatch estimates over the training set.当然,也可以只对输入-隐层进行BN,或者stack RNN中同一个time step的不同层之间做BN
- BN会引入噪声(因为是mini batch而不是整个training set),所以对于噪声敏感的方法(如RL)不太适用
BN算法思路如下(注意training和inference时候的区别)。
Layer Norm
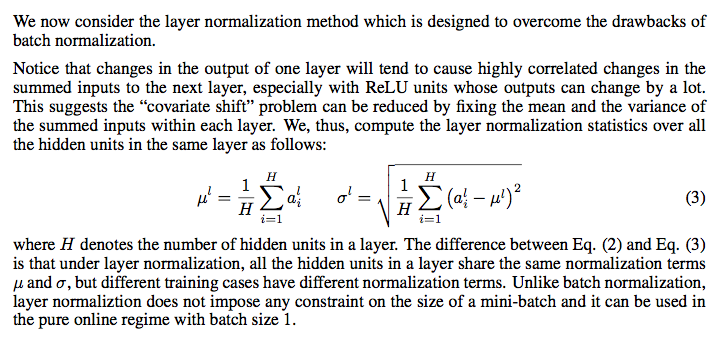
LN也是对输出归一化的。LN也是为了消除各层的covariate shift,加快收敛速度。LN相对于BN就简单多了。
- 它在training和inference时没有区别,只需要对当前隐藏层计算mean and variance就行
- 不需要保存每层的moving average mean and variance
- 不受batch size的限制,可以通过online learning的方式一条一条的输入训练数据
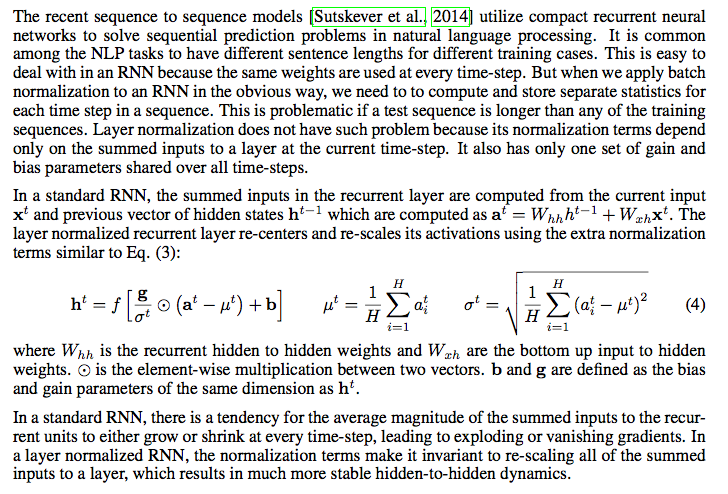
- LN可以方便的在RNN中使用
- LN增加了gain和bias作为学习的参数,μ和σ分别是该layer的隐层维度的均值和方差
Weight Norm
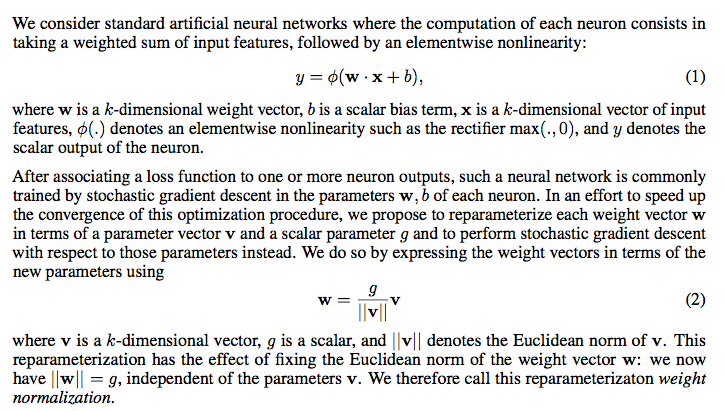
WN是使用参数重写(reparameterization weight normalization)的方法来做归一化的。哪里有weight,哪里就可以用WN来归一化。WN也是用来加速收敛的。通过对weight进行normalization,可以保证在梯度回传的时候,如果梯度越noisy(梯度越大),v的norm就越大,那么g/||v||就越小,从而就会抑制梯度。做到了梯度的自稳定(self-stabilize)。
-
与LN稍不一样,WN只有gain这一个学习参数
-
前向传播时,BN就是简单的normalization
- 梯度回传的时候,会对梯度做自稳定

- 论文里提到了WN能够让learning rate自适应/自稳定
If the learning rate is too large, the norm of the unnormalized weights grows quickly until an appropriate effective learning rate is reached. Once the norm of the weights has grown large with respect to the norm of the updates, the effective learning rate stabilizes.
- WN与BN一样,只不过BN直接从输出角度出发,WN从weight角度出发


- 注意WN的初始化,需要用第一个minibatch的均值和方差来初始化g和b。
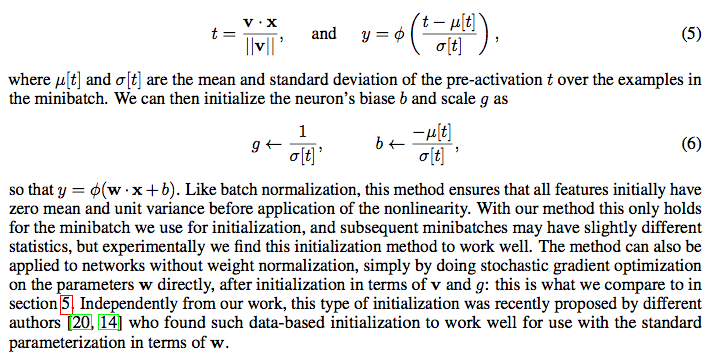
- Mean-only BN
考虑到BN并不能保证参数v的协方差矩阵为单位矩阵,也就是BN不能保证激活值与v独立。而WN能做到,因此可以结合WN与BN,此时的BN经过修改,只进行去均值操作。
selu
最理想的结果就是让每一层输出的激活值为零均值、单位方差,从而能够使得张量在传播的过程当中,不会出现covariant shift,保证回传梯度的稳定性,不会有梯度爆炸或弥散的问题。selu能够很好的实现automatically shift and rescale neuron activations towards zero mean and unit variance without explicit normalization like what batch normalization technique does.
并且可以参考References中的Selus与Leaky Relu以及Relu之间的对比。
References
Weight Normalization: A Simple Reparameterization
to Accelerate Training of Deep Neural Networks
Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift
RECURRENT BATCH NORMALIZATION
Layer Normalization
深度学习加速策略BN、WN和LN的联系与区别,各自的优缺点和适用的场景?
SELUs (scaled exponential linear units) - Visualized and Histogramed Comparisons among ReLU and Leaky ReLU
引爆机器学习圈:「自归一化神经网络」提出新型激活函数SELU