KMP算法与AC自动机
KMP算法——用于单模匹配。
AC自动机——用于多模匹配,需要了解KMP原理和Trie树。
KMP算法
KMP算法用于单模匹配,比如在一个目标串当中匹配一个模式串。暴力解法就是扫描目标串与模式串,如果发现不匹配,则目标串起始点回溯到原起始点,再后移一位,而模式串回溯到开头0。
KMP算法能够高效的找出目标串中的匹配串,相比于暴力搜索的O(m*n)的时间复杂度,KMP算法的搜索复杂度为O(m+n)。
KMP算法的基本原理
先求出next数组(数组下标表示模式子串长度,数组值表示该模式子串对应的最大公共子串长度)
举个例子,如果我们的目标串为S,匹配串为P,那么在匹配过程中,于$S_i$处失配:
\[S_0,S_1,S_2,S_3,...,S_{i-j},S_{i-j+1},...,S_i,S_{i+1},...,S_m\] \[P_0,P_1,...,P_{j-1},P{j},...\]现在假设向右移动一位模式串,此时恰好又和目标串匹配上,即为:

这说明$P_0$到$P_{j-1}$是匹配的,那么我们可以在这个P的子串中找到与该子串后缀一致的前缀,比如子串”abcab”中,前缀与后缀匹配的最大公共子串为”ab”,则我们可以将串P进行移动,使得前缀与原来的后缀对齐。
结论:当发生失配的情况下,j的新值next[j]取决于模式串中P[0]到 P[j-1]中前缀和后缀相等部分的长度, 并且next[j]恰好等于这个最大长度。
通过search查找目标串中的模式串
对比S和P,如果S[i] == P[j],则向右移动;如果S[i] != P[j],则使得j = next[j],直到S[i] == P[j]或者j == 0(即模式子串的最大公共长度为0)。当j == P.length()的时候,表示在目标串中找到了一个匹配串。
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int* getNext(string p) {
// 下标为子串长度,存储的值为最大公共长度
int* next = new int[p.length()+1];
// i和j都表示下标
int j = 0;
// 最大公共长度是指子串前缀和后缀的最大公共长度。如子串'abca'的最大公共长度为1
next[0] = next[1] = 0; // 长度为0和1的子串的最大公共长度为0(比如'abcab',长度为0时是"",长度为1时是"a")
// 遍历每个子串长度
for(int i=1;i<p.length();i++){
// 寻找最大的公共子串
while(j > 0 && p[i] != p[j])j = next[j];
// 如果对于p[i]和最大公共子串后第一个字符p[j]相同,则
if(p[i] == p[j])j++;
next[i+1] = j;
}
return next;
}
void search(string s, string p) {
int* next = getNext(p);
int j = 0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) {
while(j > 0 && s[i] != p[j]) j = next[j];
if(s[i] == p[j])
j++;
if(j == p.length()) {
cout<<"The match position is "<<i-j+1<<" to "<<i<<endl;
j = next[j];
}
}
}
int main()
{
string a = "abcdcabc";
string b = "bc";
search(a, b);
}
// 输出结果
from 1 to 2
from 6 to 7
AC自动机
AC自动机用于多模匹配。
AC自动机的基本原理
和KMP算法一样,AC自动机也是用于匹配。它的基本思路和KMP类似。
- 构建模式字典的Trie树
- 寻找Trie树中每个结点的fail指针(即KMP的next指针),即失配的时候下一个跳转的结点,和KMP一样,该指针指向root(当完全没有和当前匹配的子串后缀相同的前缀)或者指向前后缀一样且next中包含失配点的点
- 利用构建的Trie树进行搜索即可,一旦失配就通过fail指针跳转,直到重新匹配或者指向root
比如给定5个单词:say she shr he her,可以构造如下的Trie树:
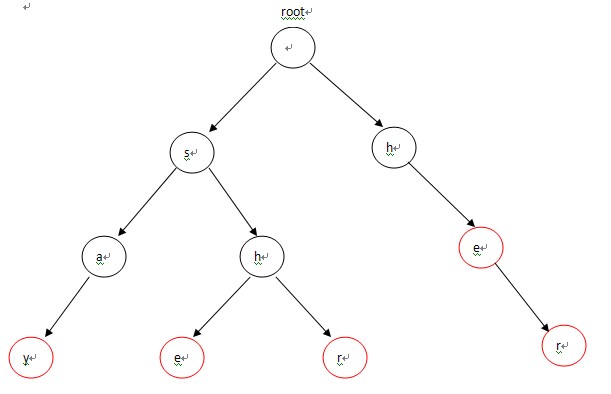
寻找每个结点的fail指针所指向的结点:
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int kind = 26;
//Trie树结点
struct Trie {
Trie* next[kind];
// 如果是一个单词,则为1
int count;
// 匹配失败的跳转指针
Trie* fail;
// 当前字符,非必要
char c;
// 该具体单词
string word;
Trie() {
count = 0;
fail = nullptr;
memset(next, 0, sizeof(next));
word = "";
c = '0';
}
};
//用于测试Trie树是否构造正确
void test(Trie* root) {
queue<Trie*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
Trie* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<kind;i++) {
if(cur->next[i] == nullptr)
continue;
Trie* tmp = cur;
tmp = tmp->next[i];
char c = (tmp->fail == nullptr)?'0':(tmp->fail->c);
cout<<tmp->c<<':'<<c<<endl;
q.push(tmp);
}
}
}
// 用于构造Trie树
void buildTrie(vector<string>& p, Trie* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
return;
for(string s : p) {
Trie* r = root;
for(auto c : s) {
if(r->next[c - 'a'] == nullptr) {
r->next[c - 'a'] = new Trie();
r->next[c - 'a']->c = c;
}
r = r->next[c - 'a'];
}
r->count++;
r->word = s;
}
}
// 创建AC自动机
void acAuto(vector<string>& p, Trie* root) {
buildTrie(p, root);
queue<Trie*> q;
if(root == nullptr)
return;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
Trie* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<kind;i++) {
if(cur->next[i] == nullptr)
continue;
if(cur == root) cur->next[i]->fail = root;
else {
Trie* p = cur->fail;
while(p != root && p->next[i] == nullptr) p = p->fail;
if(p->next[i] != nullptr) p = p->next[i];
cur->next[i]->fail = p;
}
q.push(cur->next[i]);
}
}
}
// 搜索匹配
void acSearch(vector<string>& p, string& s) {
Trie* root = new Trie();
acAuto(p, root);
Trie* r = root;
// test for trie
// test(r);
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++) {
while(r != root && r->next[s[i] - 'a'] == nullptr) r = r->fail;
if(r->next[s[i] - 'a'] != nullptr) r = r->next[s[i] - 'a'];
if(r->count > 0) {
cout<<i-r->word.size()+1<<'\t'<<i<<'\t';
cout<<r->word<<endl;
r = r->fail;
}
}
}
int main() {
string s = "asfojfdidjfdfgdiddiids";
vector<string> p;
p.push_back("did");
p.push_back("fdf");
acSearch(p, s);
}
// 输出结果
6 8 did
10 12 fdf
14 16 did