如何轻松搭建神经机器翻译模型
任务定义
给定一句英文,我们如何将它翻译成中文呢?在传统的统计方法中,我们需要对两种语言量身定制很多规则和模板。如果有一个模型,能够端到端的完成这个任务,那肯定能省不少劲的。而神经机器翻译模型恰好能够实现端到端的翻译任务,并且这个任务“天然”的符合seq2seq以及attention的框架。下面我们来简单介绍这个任务。
Simple Seq2Seq
Encoder:RNN模型
Decoder:Encoder最后一个timestep的输出作为Decoder第一个timestep的输入
Attention Seq2Seq
Encoder:RNN模型
Decoder:计算Encoder的每个timestep关于Decoder当前timestep的输入的attention值,作为真正的输入
模型实现
现在我们通过代码实现来解释如何实现一个NMT模型,并把模型放到web服务器上,以提供简单的翻译功能。在搭建模型的时候,我们需要注意模型的训练/评估与预测的方式是不同的:
- 训练/评估:decode的时候,每个decode的输入就是前一个timestep的真实输出(target)
- 预测:decode的时候,每个decode的输入是前一个timestep的预测输出(predict)
那么话不多说,让我们看看如何实现一个模型吧。
数据
我们使用的数据是中英翻译数据UM-Corpus。这个语料包含了来自多个领域的中英文对照。
指标
我们使用BLEU-4指标来表现模型的性能。指标代码采用如下:
def bleu(refs, hyps):
"""
计算bleu-4
"""
refs = [[[_ for _ in ref if _ > 0]] for ref in refs]
hyps = [[_ for _ in hyp if _ > 0] for hyp in hyps]
return nltk.translate.bleu_score.corpus_bleu(refs, hyps)
模型
preprocess
读取数据,并将中英文分开:
def data_preprocess():
train_en_corpus = []
train_ch_corpus = []
test_en_corpus = []
test_ch_corpus = []
count = 0
for dirname in ('Bilingual', 'Testing'):
if dirname == 'Bilingual':
sub_dir_names = ['Education', 'Laws', 'Microblog', 'News',
'Science', 'Spoken', 'Subtitles', 'Thesis']
for filename in sub_dir_names:
with open(os.path.join(raw_data_path, dirname, filename, ''.join(['Bi-', filename, '.txt']))) as fr:
for i, line in enumerate(fr):
line = line.strip().decode()
count += 1
if i % 2 == 0:
train_en_corpus.append(line)
else:
train_ch_corpus.append(line)
print('Finished {}'.format(count))
else:
with open(os.path.join(raw_data_path, dirname, 'Testing-Data.txt')) as fr:
for i, line in enumerate(fr):
line = line.strip().decode()
count += 1
if i % 2 == 0:
test_en_corpus.append(line)
else:
test_ch_corpus.append(line)
print('Finished {}'.format(count))
train_en_corpus = '\n'.join(train_en_corpus)
train_ch_corpus = '\n'.join(train_ch_corpus)
test_en_corpus = '\n'.join(test_en_corpus)
test_ch_corpus = '\n'.join(test_ch_corpus)
return train_en_corpus, train_ch_corpus, test_en_corpus, test_ch_corpus
分词、构造中英文词典:
def segment(corpus, tokenizer, savepath=None):
tokenized_corpus = []
count = 0
tokenized_corpus = ' '.join([_ for _ in tokenizer(corpus) if _.strip(' ')])
tokenized_corpus = tokenized_corpus.split(' \n ')
# for sentence in corpus:
# count += 1
# tokenized_corpus.append(' '.join(tokenizer(sentence)))
# if count % 1000 == 0:
# print('Finished cutting {}'.format(count))
if savepath:
with open(savepath, 'w') as fw:
pkl.dump(tokenized_corpus, fw)
return tokenized_corpus
train_en_corpus, train_ch_corpus, test_en_corpus, test_ch_corpus = data_preprocess()
train_en_corpus = segment(train_en_corpus, jieba.cut, 'data/preprocess/train_en_segment.pkl')
train_ch_corpus = segment(train_ch_corpus, lambda k: iter(k.strip()), 'data/preprocess/train_ch_segment.pkl')
test_en_corpus = segment(test_en_corpus, jieba.cut, 'data/preprocess/test_en_segment.pkl')
test_ch_corpus = segment(test_ch_corpus, lambda k: iter(k.strip()), 'data/preprocess/test_ch_segment.pkl')
def vocab(data, topK=None):
word2id = Counter()
for sentence in data:
for word in sentence.split():
word2id[word] += 1
word2id = word2id.most_common()
if topK:
word2id = word2id[:topK]
word2id, _ = zip(*word2id)
word2id = {word : i + 4 for i, word in enumerate(word2id)}
word2id['<PAD>'] = 0
word2id['<UNK>'] = 1
word2id['<S>'] = 2
word2id['</S>'] = 3
id2word = dict(zip(word2id.values(), word2id.keys()))
return word2id, id2word
en_word2id, en_id2word = vocab(train_en_corpus)
ch_word2id, ch_id2word = vocab(train_ch_corpus)
把数据中的字/词转成对应id(此时的id是根据词频排序的,词频高的词id小):
def transform(data, word2id):
ret_data = []
for sentence in data:
ret_data.append([word2id.get(word, 1) for word in sentence.split()])
return ret_data
train_en_corpus = transform(train_en_corpus, en_word2id)
train_ch_corpus = transform(train_ch_corpus, ch_word2id)
数据迭代
用于按batch读取数据。其中next_batch随机选取一个batch数据用于训练,而next则是按batch顺序读取整个数据,用于评估。
class Iterator(object):
"""
数据迭代器
"""
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = np.asarray(x)
self.y = np.asarray(y)
self.sample_num = self.x.shape[0]
def next_batch(self, batch_size):
# produce X, Y_out, Y_in, X_len, Y_in_len, Y_out_len
l = np.random.randint(0, self.sample_num - batch_size + 1)
r = l + batch_size
x_part = self.x[l:r]
y_out_part = self.y[l:r]
x_len = np.sum((x_part > 0), axis=1)
y_in_part = np.concatenate((np.ones((batch_size, 1)) * 2, y_out_part[:,:-1]), axis=-1)
max_y_dim = self.y.shape[1]
y_out_len = np.sum((y_out_part > 0), axis=1) + 1
y_out_len = np.min(np.concatenate([np.ones((batch_size, 1)) * max_y_dim, y_out_len.reshape(-1, 1)], axis=-1), axis=-1)
y_in_len = np.sum((y_in_part > 0), axis=1) + 1
y_in_len = np.min(np.concatenate([np.ones((batch_size, 1)) * max_y_dim, y_in_len.reshape(-1, 1)], axis=-1), axis=-1)
x_len = x_len.astype(np.int32)
y_in_part = y_in_part.astype(np.int32)
y_in_len = y_in_len.astype(np.int32)
y_out_len = y_out_len.astype(np.int32)
return x_part, y_out_part, y_in_part, x_len, y_in_len, y_out_len
def next(self, batch_size):
l = 0
while l < self.sample_num:
r = min(l + batch_size, self.sample_num)
batch_size = r - l
x_part = self.x[l:r]
y_out_part = self.y[l:r]
x_len = np.sum((x_part > 0), axis=1)
y_in_part = np.concatenate((np.ones((batch_size, 1)) * 2, y_out_part[:,:-1]), axis=-1)
max_y_dim = self.y.shape[1]
y_out_len = np.sum((y_out_part > 0), axis=1) + 1
y_out_len = np.min(np.concatenate([np.ones((batch_size, 1)) * max_y_dim, y_out_len.reshape(-1, 1)], axis=-1), axis=-1)
y_in_len = np.sum((y_in_part > 0), axis=1) + 1
y_in_len = np.min(np.concatenate([np.ones((batch_size, 1)) * max_y_dim, y_in_len.reshape(-1, 1)], axis=-1), axis=-1)
x_len = x_len.astype(np.int32)
y_in_part = y_in_part.astype(np.int32)
y_in_len = y_in_len.astype(np.int32)
y_out_len = y_out_len.astype(np.int32)
l += batch_size
yield x_part, y_out_part, y_in_part, x_len, y_in_len, y_out_len
模型构造
class NMTModel(object):
"""
带Attention的NMT模型
"""
def __init__(self,
src_max_vocab_size,
tgt_max_vocab_size,
embedding_size,
hidden_size,
src_max_seq_len,
tgt_max_seq_len,
tgt_start_id,
tgt_end_id,
max_gradient_norm=5,
maximum_iterations=None,
optimizer='adam',
):
self.initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer(
-0.05, 0.05)
self.optimizer = optimizer
# 源词表大小
self.src_max_vocab_size = src_max_vocab_size
# 目标词表大小
self.tgt_max_vocab_size = tgt_max_vocab_size
# 输入embedding大小(src与tgt的embedding_size可以不同)
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
# 隐层大小
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
# 源序列长度
self.src_max_seq_len = src_max_seq_len
# 目标序列长度
self.tgt_max_seq_len = tgt_max_seq_len
# 目标序列起始id(输入的初始id值)
self.tgt_start_id = tgt_start_id
# 目标的终结id(模型预测到该id后停止预测)
self.tgt_end_id = tgt_end_id
if maximum_iterations is None:
self.maximum_iterations = self.tgt_max_seq_len
else:
self.maximum_iterations = maximum_iterations
self.max_gradient_norm = max_gradient_norm
self.add_placeholders()
self.batch_size = tf.shape(self.X)[0]
self.add_embeddings()
self.encoder()
self.decoder()
self.add_loss()
self.add_train_op()
def add_placeholders(self):
# X, Y_out, Y_in, X_len, Y_in_len, Y_out_len
self.X = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, None])
self.Y_out = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, None])
self.Y_in = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, None])
self.X_len = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, ])
self.Y_in_len = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, ])
self.Y_out_len = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, ])
self.lr = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
self.dropout = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
def add_embeddings(self):
with tf.variable_scope('embeddings', initializer=self.initializer):
self.X_emb = tf.get_variable('X_emb',
shape=(self.src_max_vocab_size, self.embedding_size),
dtype=tf.float32)
self.Y_emb = tf.get_variable('Y_emb',
shape=(self.tgt_max_vocab_size, self.embedding_size),
dtype=tf.float32)
self.encoder_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.X_emb, self.X)
self.decoder_input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.Y_emb, self.Y_in)
def encoder(self):
with tf.variable_scope('encoder'):
fw_encoder_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell(self.hidden_size)
fw_encoder_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(fw_encoder_cell, input_keep_prob=1-self.dropout)
bw_encoder_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell(self.hidden_size)
bw_encoder_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(bw_encoder_cell, input_keep_prob=1-self.dropout)
encoder_outputs, bi_last_state = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(
fw_encoder_cell, bw_encoder_cell, self.encoder_input,
self.X_len, dtype=tf.float32)
self.encoder_outputs = tf.concat(encoder_outputs, axis=-1)
self.encoder_last_state = bi_last_state
def decoder(self):
with tf.variable_scope('decoder'):
decoder_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell(self.hidden_size)
decoder_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(decoder_cell, input_keep_prob=1-self.dropout)
attention_mechanism = tf.contrib.seq2seq.LuongAttention(
self.hidden_size, self.encoder_outputs,
memory_sequence_length=self.X_len)
decoder_cell = tf.contrib.seq2seq.AttentionWrapper(
decoder_cell, attention_mechanism,
attention_layer_size=self.hidden_size)
projection_layer = layers_core.Dense(
self.tgt_max_vocab_size, use_bias=False)
# 训练或评估的时候,decoder的output是真实的target,input是target右移一个词
with tf.variable_scope('dynamic_decode'):
# Helper
helper = tf.contrib.seq2seq.TrainingHelper(
self.decoder_input, tf.ones((self.batch_size, ), dtype=tf.int32) * self.tgt_max_seq_len, time_major=False)
# Decoder
decoder_initial_state = decoder_cell.zero_state(self.batch_size, dtype=tf.float32).clone(
cell_state=self.encoder_last_state[0])
decoder = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BasicDecoder(
decoder_cell, helper, decoder_initial_state,
output_layer=projection_layer)
# Dynamic decoding
outputs, _, _ = tf.contrib.seq2seq.dynamic_decode(decoder)
self.logits = outputs.rnn_output
self.pred = tf.argmax(self.logits, axis=2)
# 预测的时候,decoder的每个timestep的输入为前一个时刻的输出
with tf.variable_scope('dynamic_decode', reuse=True):
# Helper
helper = tf.contrib.seq2seq.GreedyEmbeddingHelper(
self.Y_emb,
start_tokens=tf.fill([self.batch_size], self.tgt_start_id),
end_token=self.tgt_end_id)
decoder_initial_state = decoder_cell.zero_state(self.batch_size, dtype=tf.float32).clone(
cell_state=self.encoder_last_state[0])
# Decoder
decoder = tf.contrib.seq2seq.BasicDecoder(
decoder_cell, helper, decoder_initial_state,
output_layer=projection_layer)
# Dynamic decoding
outputs, _, _ = tf.contrib.seq2seq.dynamic_decode(
decoder, maximum_iterations=self.maximum_iterations)
self.translations = outputs.sample_id
def add_loss(self):
target_weights = tf.sequence_mask(
self.Y_out_len, self.tgt_max_seq_len, dtype=self.logits.dtype)
crossent = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=self.Y_out, logits=self.logits)
self.loss_op = (tf.reduce_sum(crossent * target_weights) / tf.to_float(self.batch_size))
def add_train_op(self):
params = tf.trainable_variables()
gradients = tf.gradients(self.loss_op, params)
clipped_gradients, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(
gradients, self.max_gradient_norm)
# Optimization
if self.optimizer == 'sgd':
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(self.lr)
elif self.optimizer == 'adadelta':
optimizer = tf.train.AdaDeltaOptimizer(self.lr)
else:
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(self.lr)
self.global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False, name='global_step')
self.train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(
zip(clipped_gradients, params), global_step=self.global_step)
训练模型
def train():
# load data and dictionary
with open('data/preprocess/vocab_dict_and_corpus.pkl') as fr:
en_word2id, en_id2word, ch_word2id, ch_id2word, \
train_en_corpus, train_ch_corpus, test_en_corpus, test_ch_corpus = pkl.load(fr)
train_en_corpus = padding(train_en_corpus, src_max_seq_len)
train_ch_corpus = padding(train_ch_corpus, tgt_max_seq_len)
# truncate the vocabrary
# for the words exceeded te vocab size, we set it as 1(<UNK>)
train_en_corpus[train_en_corpus >= src_max_vocab_size] = 1
train_ch_corpus[train_ch_corpus >= tgt_max_vocab_size] = 1
train_en_corpus, eval_en_corpus, train_ch_corpus, eval_ch_corpus = train_test_split(train_en_corpus, train_ch_corpus, test_size=0.2, )
print('train size:{}, val size:{}'.format(train_en_corpus.shape, eval_en_corpus.shape))
iter_num = train_en_corpus.shape[0] // batch_size + 1
data_iterator = Iterator(train_en_corpus, train_ch_corpus)
eval_data_iterator = Iterator(eval_en_corpus, eval_ch_corpus)
now_lr = lr
with tf.Session(config=cf) as sess:
model = NMTModel(src_max_vocab_size=src_max_vocab_size,
tgt_max_vocab_size=tgt_max_vocab_size,
embedding_size=embedding_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
src_max_seq_len=src_max_seq_len,
tgt_max_seq_len=tgt_max_seq_len,
tgt_start_id=tgt_start_id,
tgt_end_id=tgt_end_id,
max_gradient_norm=max_gradient_norm,
maximum_iterations=maximum_iterations,
optimizer=optimizer)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
for epoch in xrange(num_epochs):
for iter_n in xrange(iter_num):
X, Y_out, Y_in, X_len, Y_in_len, Y_out_len = data_iterator.next_batch(batch_size)
# print(X.shape)
# print(Y_out.shape)
# print(Y_in.shape)
# print(X_len.shape)
# print(Y_in_len.shape)
# print(Y_out_len.shape)
loss, _, global_step = sess.run([model.loss_op, model.train_op, model.global_step],
feed_dict={ model.X:X,
model.Y_out:Y_out,
model.Y_in:Y_in,
model.X_len:X_len,
model.Y_in_len:Y_in_len,
model.Y_out_len:Y_out_len,
model.lr:now_lr,
model.dropout:dropout})
if iter_n % 100 == 0:
print('iter:{}, train loss:{}'.format(iter_n, loss))
if optimizer == 'sgd':
now_lr = now_lr / 2
evaluate(model, sess, eval_data_iterator)
saver.save(sess,'model/my_model', global_step=global_step)
评估模型
def evaluate(model, sess, data_iterator):
translations = []
refs = []
losses = []
for X, Y_out, Y_in, X_len, Y_in_len, Y_out_len in data_iterator.next(batch_size):
loss, translation = sess.run([model.loss_op, model.translations],
feed_dict={ model.X:X,
model.Y_in:Y_in,
model.Y_out:Y_out,
model.X_len:X_len,
model.Y_in_len:Y_in_len,
model.Y_out_len:Y_out_len,
model.lr:lr,
model.dropout:0.})
translations.append(translation)
refs.append(Y_out)
losses.append(loss)
translations = np.concatenate(translations, axis=0)
refs = np.concatenate(refs, axis=0)
bleu_score = bleu(refs, translations)
print('bleu score:{}, loss:{}'.format(bleu_score, np.mean(loss)))
预测(可用于线上服务)
def predict(X):
with open('data/preprocess/vocab_dict.pkl') as fr:
en_word2id, en_id2word, ch_word2id, ch_id2word = pkl.load(fr)
if type(X) == str:
X = X
elif type(x) == list or type(X) == tuple:
X = '\n'.join(X)
else:
raise ValueError('You must ensure the `X` be string or list!')
X = segment(X, jieba.cut)
X = transform(X, en_word2id)
X = padding(X, src_max_seq_len)
X_len = np.sum((X > 0), axis=1)
# X -> (src_max_seq_len, ) or (batch, sec_max_seq_len, )
with tf.Session(config=cf) as sess:
model = NMTModel(src_max_vocab_size=src_max_vocab_size,
tgt_max_vocab_size=tgt_max_vocab_size,
embedding_size=embedding_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
src_max_seq_len=src_max_seq_len,
tgt_max_seq_len=tgt_max_seq_len,
tgt_start_id=tgt_start_id,
tgt_end_id=tgt_end_id,
max_gradient_norm=max_gradient_norm,
maximum_iterations=maximum_iterations,
optimizer=optimizer)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint('model/'))
translations = sess.run(model.translations,
feed_dict={ model.X:X,
model.Y_out:[[]],
model.Y_in:[[]],
model.X_len:X_len,
model.Y_in_len:[],
model.Y_out_len:[],
model.lr:lr,
model.dropout:0.})
translations = transform2word(translations, ch_id2word)
return translations
完整工程代码
完整代码可以参考:nmt。
训练与评估结果
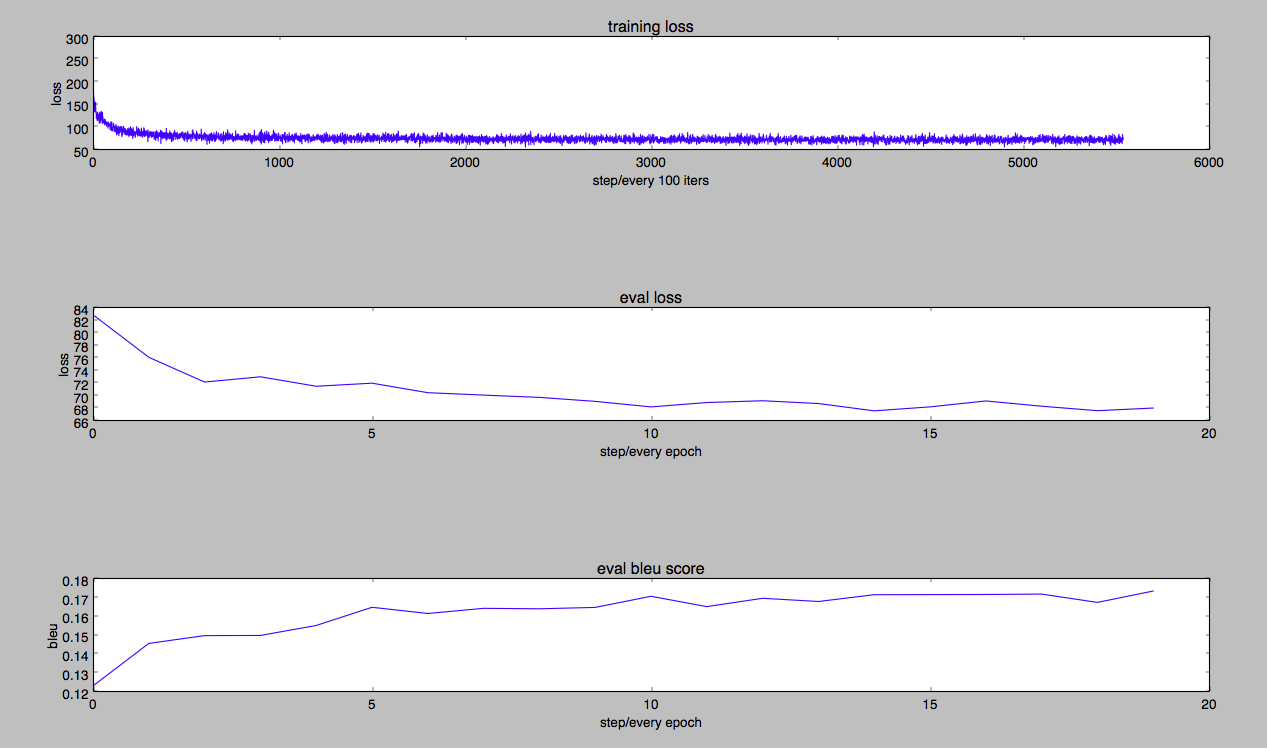
因为忘了加summary到Tensorboard上,所以最后自己根据log日志画图。从下图看,training loss也是波动下降到收敛,eval loss也趋于平稳,最后bleu值在0.17左右,最高达到0.173695055726(在最后一个epoch)。实验只训练了20轮,模型结构、参数也相对简单,所以最后分数不是很高,不过从线上效果来看还是“有模有样”的。
线上结果
网页页面显示如下:

可以看到,上面输入一个比较简单的英文句:
I would like to play with you.
对应的中文翻译可以得到:
我想跟你一起玩<PAD>